New Generation Press Hardened Steels Research by General Motors
New Generation Press Hardened Steels Research by General Motors
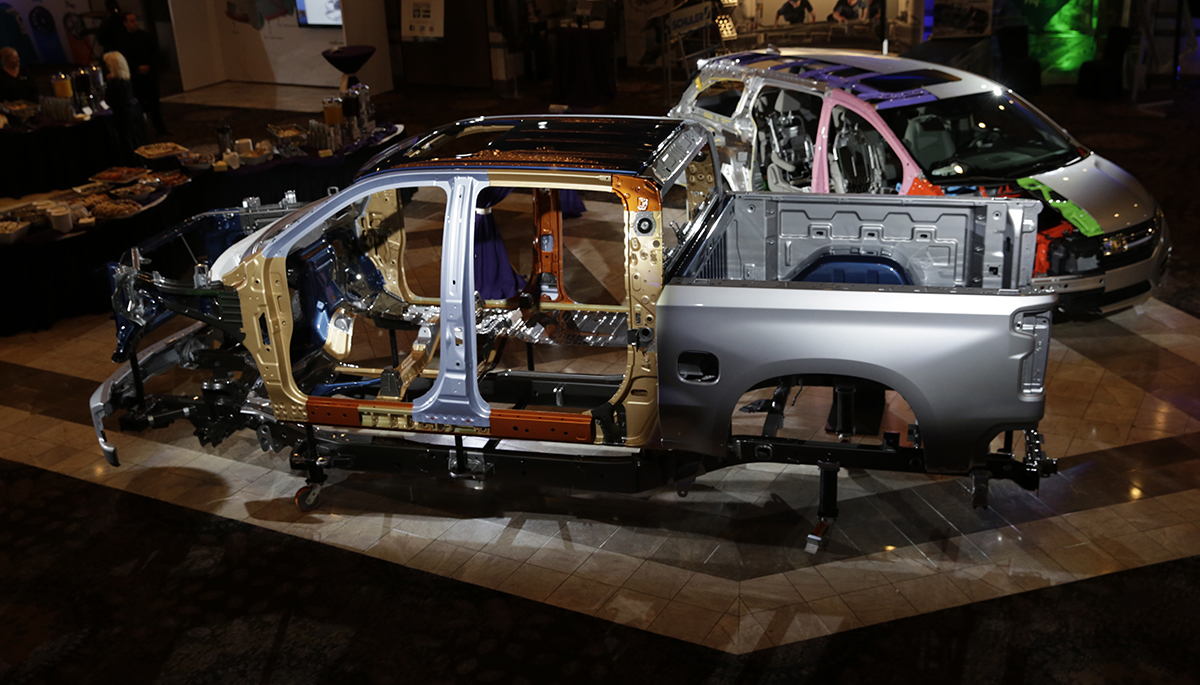
2019 Chevrolet Silverado BIW
AISI Automotive Webinar:
New Generation Press Hardened Steels – with Tensile Strength ranging from 1.7-2.0 GPa and Enhanced Bendability
Tuesday September 29th @ 9:00-10:00am ET
Complimentary Registration @ AISI
Register Now
AISI welcomes special guest presenter Jeff Wang – Site Leader, General Motors China Science Lab and Manager, Structural Metallic Systems Research.
Press hardened steels (PHS) are widely used today for automotive body structure components to increase occupant safety and reduce mass for improved fuel economy.
“As lightweighting continues to be a design imperative for the automotive industry, it is desired to adopt more press hardened components with higher tensile strengths while maintaining adequate  fracture resistance” according to Jeff Wang, Manager of Structural Metallic Systems Research, General Motors Global Research and Development. “We have been exploring new press hardened steels with tensile strength of 1.7-2.0 GPa.”
fracture resistance” according to Jeff Wang, Manager of Structural Metallic Systems Research, General Motors Global Research and Development. “We have been exploring new press hardened steels with tensile strength of 1.7-2.0 GPa.”
The most commonly used PHS grade is the boron-containing 22MnB5 with 0.22% Carbon by weight, good bendability and ultimate tensile strength of approximately 1.5 GPa. In this presentation engineers and designers will hear about two new press hardened steels being investigated by GM and learn about their properties compared to those of the commercialized 22MnB5.
- The first steel, 34MnBV, is coated with a thin aluminum silicon coating and it contains 0.35% Carbon by weight and Vanadium as a micro-alloying element. Its ultimate tensile strength approaching 2.0 GPa is achieved with a bending angle of about 55 degrees at 1.4 mm gage according to the VDA 238-100 test standard.
- The second steel, 20MnCr, has about 0.20% Carbon by weight and an additional combination of Chromium and Silicon for oxidation resistance. It has an ultimate tensile strength of 1.7 GPa with a bending angle above 55 degrees at 1.4 mm thickness. This steel does not have any pre-coating, and yet it is oxidation resistant at high temperature, thus no shot blasting would be required after hot stamping.
Performance evaluations relevant to automotive applications, such as weldability and corrosion, have been conducted on samples from industrial coils.
Register now to reserve your seat for this informative webinar and hear why GM continues to explore new press hardened steels for future body structures to reduce mass, improve fuel economy and emissions, and to increase occupant safety. This webinar along with others in our series (GDIS) is presented complimentary to the automotive engineering and educational community by AISI.
For more information or to register contact AISIwebinars@www.steel.org.
Link for GoToWebinar registration: https://attendee.gotowebinar.com/register/4797541276278043915
![[AISI LOGO]](https://www.steel.org/wp-content/themes/steel-org/assets/images/steel-logo.png) American
Iron and Steel
Institute
American
Iron and Steel
Institute